Digital Signal Processing Basics
What is Digital Signal Processing?
Virtually any song you can listen to on the radio has examples of Digital Signal Processing.
But let me not get ahead of myself, let me start with a simple definition of what Digital Signal Processing (or DSP for short) is:
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) -the manipulation, analysis, and transformation of signals, which are typically represented as sequences of numbers, using digital computing techniques. It involves applying mathematical operations to these numerical representations to extract information, enhance features, or modify the signal in some way to achieve desired outcomes.
Since this definition is on the wordier side, let me break it down a little bit for you. Let’s start with the word signal, when we talk about audio signals, we define it as a detectable physical quantity or impulse (such as a voltage, current, or magnetic field strength) by which messages or information can be transmitted.
In this case the information we want to manipulate in DSP are the binary representations of the analog audio signal. This is because the modern computers you use every day to perform actions such as DSP need discrete values, unlike the infinite values you find in analog signals.
This is where an analog to digital converter comes in.
ADC and DAC

ADC, a bilingual interpreter who can speak both languages, takes in the analog signal from something such as a microphone and converts it to a digital signal, the language of the computer. It does this by extracting tiny sliced samples thousands of times per second, the rate at which is done is called the sampling rate. This data can then be together and spit out the other side to be translated in the reverse back into analog with the help of ADC’s opposite, the Digital Audio Converter (DAC). In between these two processes, we have a lot of creative freedom on what we can do to manipulate these samples.
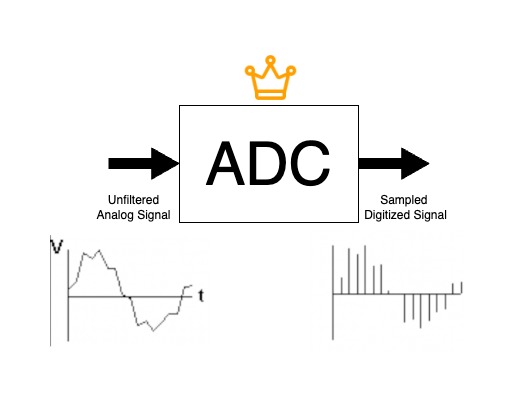
This in between processing is DSP.
Although we talk about DSP primarily in between the ADC and DAC there is still some DSP happening within the ADC and DAC tHemselves. Within the ADC, there sometimes is an antialias filter and within the DAC there is sometimes a reconstruction filter.

The other definition that is commonly used for DSP is the process of analyzing and modifying a signal to optimize or improve its efficiency or performance.While you can use DSP to achieve the results, this isn’t the only thing it can be used for, Sometimes you just want things to sound cool ,Sometimes you want things to sounds weird, It’s all up to you and your imagination!
Here are just Some of the things you can do that are considered DSP:
Compression:

Controls the dynamic range of a sound. This means that it decreases the variance between the highest and lowest amplitudes of an audio signal by either reducing the loudest parts aka downward compression), or increasing the quietest parts aka (upward compression). This helps to make sure all the desired notes in an audio recording can be heard clearly.
Filtering:

A filter lowers or completely cuts unwanted frequencies from an audio signal. This can be done to a large amount of frequencies such as a High Pass Filter, which cuts lower frequencies and preserves the higher ones, or the Opposite called a low pass filter which cuts higher frequencies and preserves lower ones
We also have band pass filters which only allows frequencies within a certain range to pass through and band stop filters in which everything is passed through except the band of frequencies around the desired cutoff.
Modulation:

Modulation is a process of varying an aspect of an original signal by another signal. There are two main kinds of modulation called Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation.
Amplitude modulation is when the amplitude of the carrier wave is modified in order to send the data or information.
Frequency Modulation is when the frequency of the carrier wave is modified in order to send the data or information.
Conclusion
I hope this blog post helped you learn a little something about DSP.
Now go forth and make weird sounds!
Sources
1 - Analog Devices - A Beginner’s Guide to Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
2 - Zola, Andrew - TechTarget - Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
3 - Geeks For Geeks (2024)- Difference between Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
