Out-Of-The-Box Sound Sources for your IMS
Sometimes you don’t want to design the audio generating source completely from scratch in your up-coming Interactive Music System (IMS). Sometimes you’ve already put enough weight on your shoulders in knitting and stuffing your kawaii panda-shaped instrument or planing and polishing your pieces of oak for your pirate treasure chest-themed music box. Don’t despair! There is vendors making synthesizers who speak openly in voltages – just patch in and have a listen. Maybe you’d like some of them to produce the soothing sounds lacking in your system?
Below is a non-exhaustive survey of a few embedded systems and synthesizers who could possibly speak together through jumper cables.
Embedded Systems
Embedded systems are small computer systems consisting of computer processor and memory along with I/O pins for communication with the outside world. These pins could be dedicated analog inputs, dedicated analog outputs, or digital I/O’s. An embedded system would typically have a combination of different general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins. These connectors typically operate with voltages of either 5V or 3.3V.
Let us not forget that audio in/out jacks essentially are analog I/O connectors as well!
Pssst – Keep in mind that it can be possible to simulate extra analog outputs by applying Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to a digital output (which has a state of either 0 or 1). You can read more about PWM here.
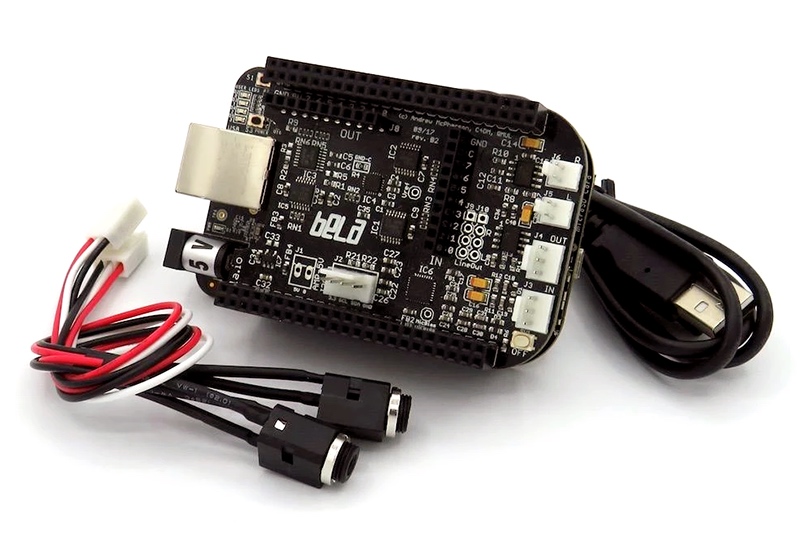
Bela
Bela is the embedded system of choice at MCT, because of it’s super low latency (0.5ms action-to-sound latency), and a generous amount of I/O pins. This is a complete system for creating an IMS, where Pure Data is one of the programming languages supported.
I/O
- 2x Audio Inputs
- 2x Audio Outputs
- 8x 16-bit Analog Inputs
- 8x 16-bit Analog Outputs
- 16x Digital I/O
- 2x 1W 8ohm Speaker Outputs
The Bela is capable of software PWM on all 16 digital outputs (at once). But since the Bela’s internal “clock” is set to 44.1 kHz, this would work best for control voltage (CV) signals.
If you want 8-bit resolution you would need to allow 256 samples per PWM period, for a PWM frequency of roughly 172 Hz.
– ryjobil
Sampling Rates and Bit Depth
Below is a table of the sampling rates and bit depths of the Bela’s different I/O pins.
| I/O | Sampling Rate | Bit Depth |
|---|---|---|
| Audio | 44.1 kHz | 16-bit |
| Analog | 22.05 kHz | 16-bit |
| Digital | 44.1 kHz | n/a |
Voltage Levels
It is extremely important to keep voltage ranges in mind, and know the voltage tolerances of the different connector types, as to not fry anything!
In plain words: Do not connect 5V directly to a digital input!
| Signal | Voltage Range | Voltage Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Digital I/O | 0-3.3V | 3.3V |
| Analog Input | 0-4.096V | 5V |
| Analog Output | 0-5V | 5V |
Other Systems
There are alternatives to Bela, in which I’ll mention a few embedded systems with GPIO pins for inter-connectivity.
Arduino Uno
- 14x Digital I/O (of wich 6 provide PWM output)
- 6x Analog Input
The Arduino Uno operates within 5V.
Raspberry Pi 4
- 26x Digital I/O (of which 4 provide PWM output) There are two channels of PWM which also can provide audio output
The Raspberry Pi 4 operates within 3.3V.
Flipper Zero
- 8x Digital I/O
- of which 6 inputs can be assigned to a 12-bit ADC channel
- of which 8 outputs provide PWM
The Flipper Zero operates within 3.3V.
External Synthesizers
Synthesizers use Control Voltage (CV) between it’s internal modules to operate – a perfect match for our embedded systems! Let’s look into the specifications of a few pocket-sized (give or take) semi-modular synthesizers which uses jumper cables for patching.
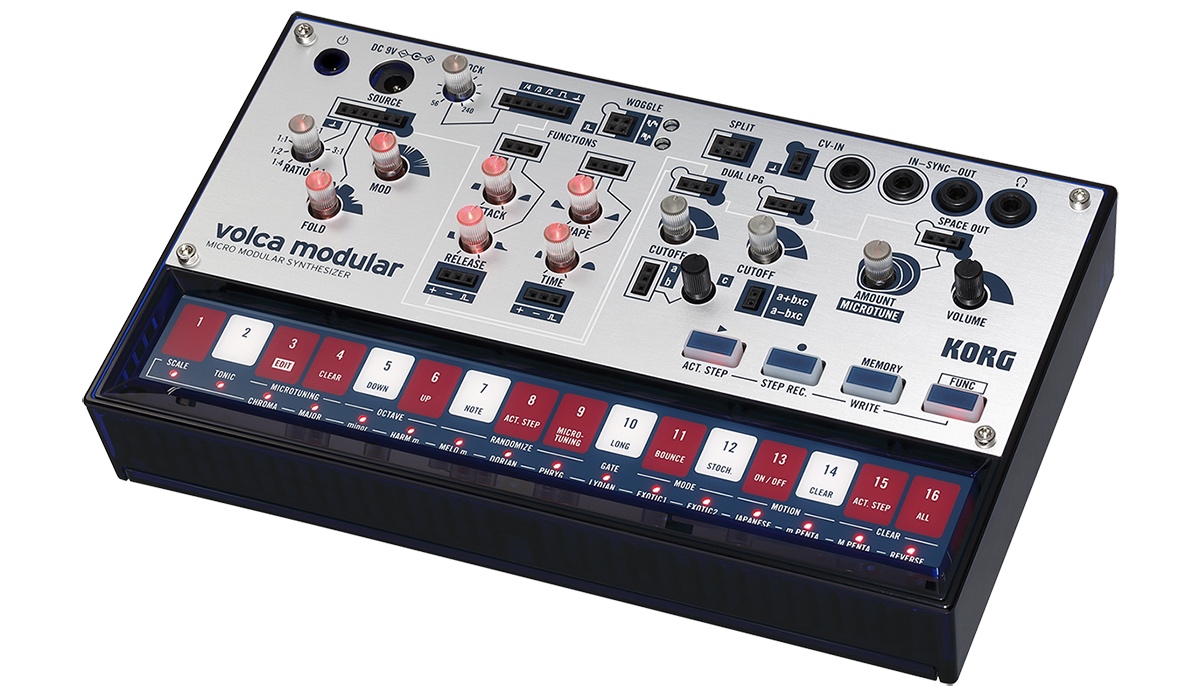
Korg Volca Modular
The Korg Volca Modular is a West Coast (Buchla) style analog synthesizer. To connect with Eurorack-style synthesizers, it supports two CV inputs through a 3.5mm TRS with the following channels:
1) Left: Clipped to +/-5V and converted to +/-3.3V 2) Right: Expects a 1V/octave signal (0-6V) converted to internal pitch offset voltage control
However, we’ll just bypass that limited and connect straight to one of the 50 patch points.
The Korg Volga Modular operates within 3.3V.

Moog Werkstatt-01
The Moog Werkstatt-01 is an traditional East Coast style analog semi-modular synthesizer that comes shipped as a kit. This instrument uses jumper cables for patching, although it usually ships with a mountable CV expander, who’ll transform the 20x pin I/O interface to one with 12x 3.5mm TS jack connectivity. Of course we’ll keep all 20 of them, not just “12 of the most useful inputs”.
For the adventurous, there’s an easter egg under the hood:
Test Points, Jumpers, and a mini 16 x 6 Experimenter’s pad are provided on the Werkstatt Printed Circuit Board.
The Moog Werkstatt-01 operates within 5V.

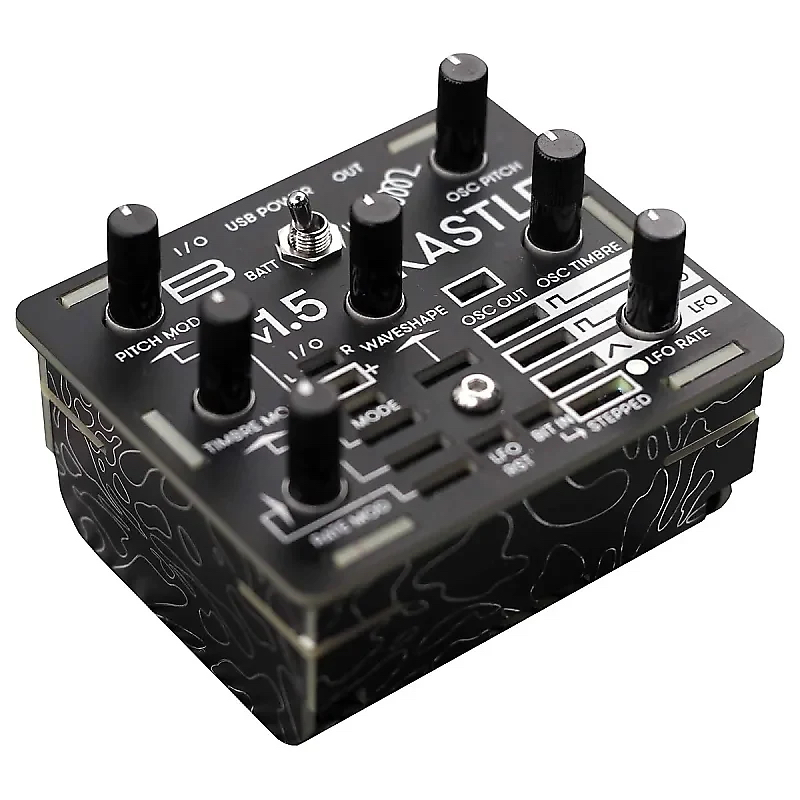
Bastl Kastle & Bastl Kastle Drum
The Bastl Kastle & Bastl Kastle Drum essentially share the same internal hardware, but with different firmware and exterior design. These are strange, noisy, glitchy, experimental digital modular synthesizers made for exploration. They’re controlled by two Attiny 85’s, one acting as a VCO (for sound generation) and the other as a LFO (for sound modulation). These can be reprogrammed with an Arduino.
For traditional CV sharing, they sport a 3.5mm TRS jack I/O which can be freely routed. For our purpose, we’ll make use of the 36 pin I/O’s (of which two are linked to the jack I/O).
The Kastl’s operate within 5V.

Start Connecting
Now you have some ideas for “out-of-the-box” sound generation in your IMS. In an upcoming blogpost for my IMS project, I will present how I made use of a Bela and a Bastl Kastle in beautiful(?) harmony!
Disclaimer
Don’t try this at home! Or, well, please do. But play with this at your own discretion.
The information and specifications presented in this blogpost is correct to the best of the authors knowledge, but the they take no responsibility for any fried Bela-boards or any other damage caused by applying this information to the real synthesized world. Respect voltage tolerances!
Happy patching!
